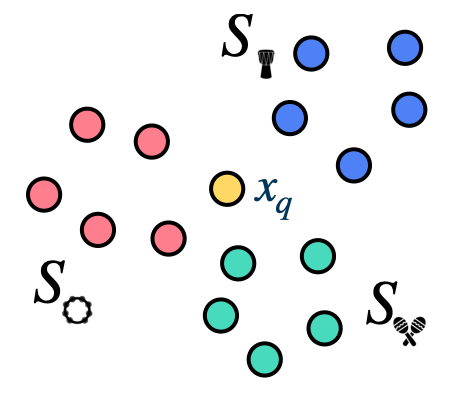Classification: Sound Event Detection
Classification: Sound Event Detection#
While most of the few-shot classification works focus on solving K-way N-shot problems (e.g. 5-way 5-shot, 5-way 1-shot), it is not very straightforward to connect these problems to a real-world application scenario. Wang et al. instead applied FSL to sound event detection where the goal is to build a Ctrl-F for audio events [39]. In the envisioned paradigm, the user provides a few examples of the target, the model then automatically locates similar-sounding events within a recording.
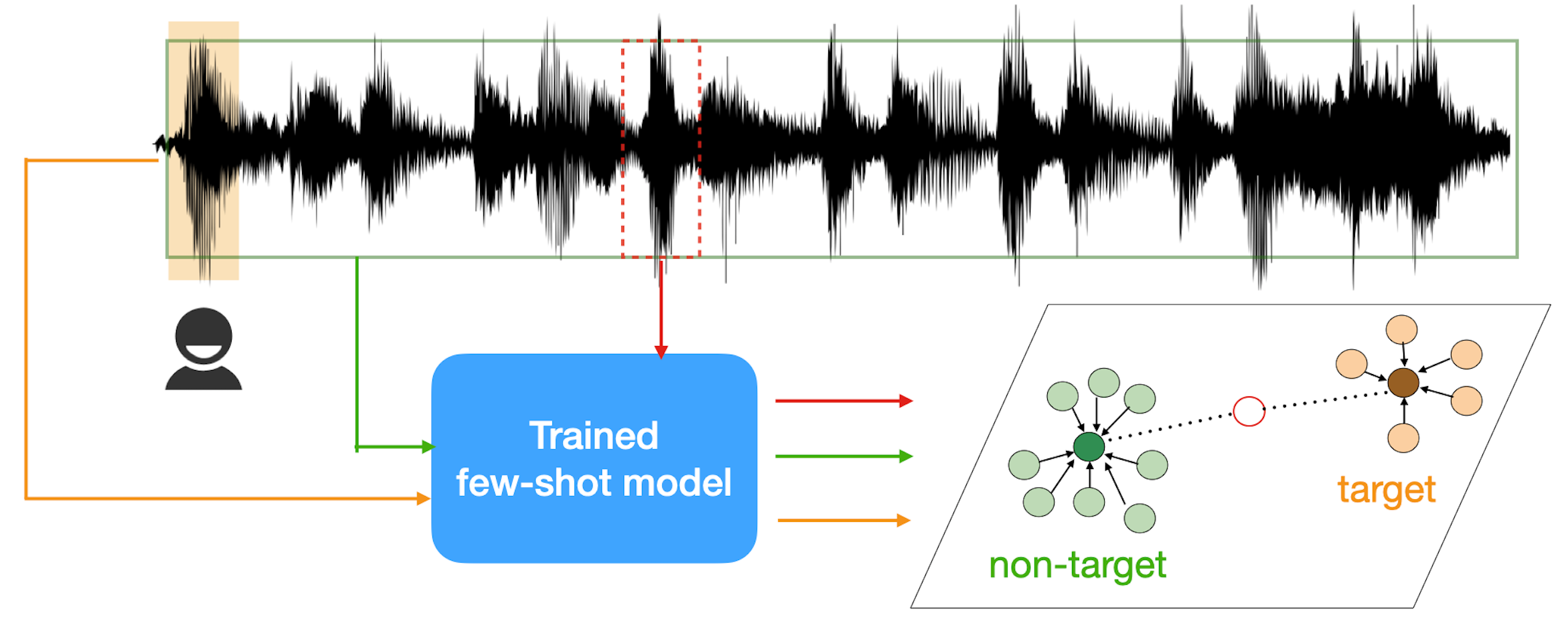
To do so, they first pre-trained a prototypical network [16] on standard K-way N-shot episodes. At test time, the user would provide a few target examples as the support set to compute the target prototype. To model the non-target class, they proposed to take the entire query recording as the support set to compute the non-target prototype with the assumption that the target class is relatively sparse. Therefore, no addidional labels are required from the user.
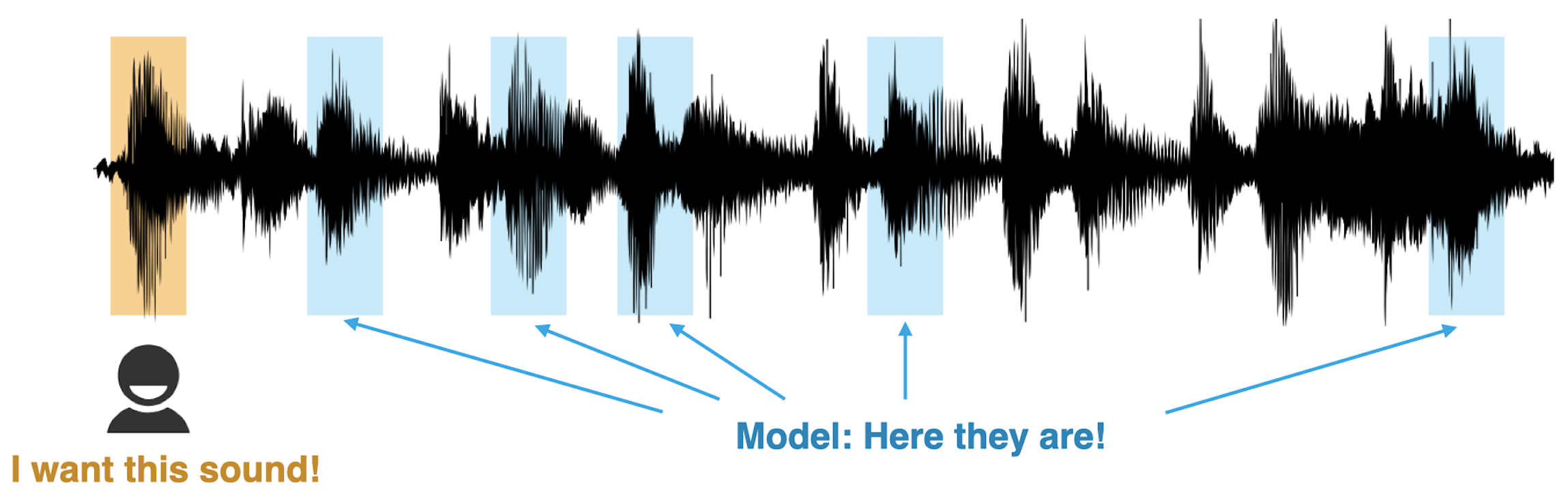
The proposed paradigm is evaluated on speech to perform few-shot keyword spotting and shows promising results on both seen and unseen languages. Note that there is nothing speech-specific about the method so the technique and findings should be applicable to other audio domains such as music, bioacoustics, and environmental sound.